Curious how to inspire your students with AI creativity while also guiding them to be responsible digital citizens? Teaching AI and digital citizenship skills is a a powerful combination that prepares students to be both creative and responsible digital citizens.

With TechnoKids’ newest release, TechnoFuture AI, learners step into the role of futurists by designing an interactive digital story about tomorrow’s world. As they explore imaginative technologies, they experiment with generative AI tools to write compelling text, create original images, compose music, and even make 3D models.
But TechnoFuture AI goes beyond creativity. Students also develop essential digital citizenship skills. They learn that innovation must be paired with responsibility. They examine the principles of copyright, fair use, and derivative works to understand how to respect the work of others while crafting their own. By blending exciting hands-on AI activities with lessons in ethical technology use, the course empowers students to be both creators and conscientious digital citizens.
Futuristic Storytelling
Students become futurists as they design an interactive “Choose Your Own Adventure” digital story. They imagine a day in the life of a teen in the future and invent gadgets to make the morning routine easier—maybe a bed that makes itself, a wardrobe that selects clothing, or a kitchen device that prepares breakfast.
The adventure continues with creative ways to get to school. Will students dream up a hoverboard with safety features, a flying rocket car, or a jet-powered backpack with collision sensors? Their inventions bring their science fiction story to life.

AI-Powered Idea Generation
To spark creativity, students learn how to write detailed and specific text prompts for large language models like ChatGPT, Copilot, or Gemini. With the help of AI, they brainstorm vehicle names, safety features, and imaginative details to enrich their story.
From Images to 3D Models
Next, students search for visual prompts to turn futuristic vehicles into 3D models. Starting with an inspiring image, they will be using generative AI to transform concepts into objects that enhance their digital story.
But First: Teaching AI and Digital Citizenship
Not every image online can be copied and reused. This is where students learn that generative AI is powerful, but creativity must also be responsible. The course guides them through the importance of copyright, fair use, and respecting original work – skills that prepare them to be both imaginative and ethical digital citizens.
Students explore the concept of a derivative work. This is a new creation made by transforming an existing work into something different. They learn that it is against copyright law to take someone’s work and change it without permission or giving credit.
Before finding the ‘right’ picture for their stories, students examine Creative Commons (CC) licenses – public copyright that states how a work can be used. They must check the license for the image that they want to save and remix. Does the license allow for personal use, such as in school projects? Do they know if they must give credit to the original creator?
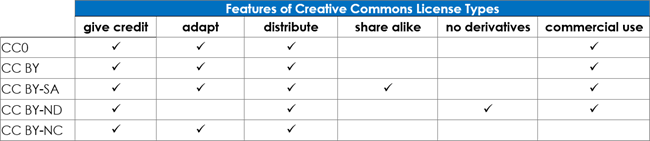
In this activity, students study Creative Commons Licenses. Codes show what they can and cannot do:
- BY (Attribution): Means ‘by the creator’. The original creator must be given credit.
- SA (Share Alike): If the work is changed or remixed the new creation must be shared using the same license as the original.
- ND (No Derivatives): No changes or adaptations are permitted to the original work.
- NC (No Commercial Use): Only personal use is permitted.
Applying Copyright and Fair Use
Now students are ready to find a visual prompt: an image that a generative AI system can use as a reference to produce a new creation – their 3D model.
To match their creative vision, they search for a suitable vehicle image using tools such as Google Image Search or open-license communities like Pixabay to find a vehicle image that suits their story.
But this stage is about more than just picking an image. Students learn that every image comes with rules for use, and it is their responsibility to follow them. They review copyright or license details, explain why their chosen image is permitted, and identify if the creator requires credit.
Teaching AI and Digital Citizenship – Copyright Checklist
Before you use an online image:
- Find an image (Google Images/Pixabay/other source)
- Check license terms (Is it free? Does it allow remixing? Can you use it in a class project?)
- Decide what to do –
- ✔ Use it and give credit if required
- ❌ Don’t use it if permission is missing
As with all TechnoKids courses, optional activities are provided for teachers who want to extend or reinforce learning. In this session, there is a Skill Review that gives students the chance to deepen their understanding of usage rights. They explore the License and Terms of Service of Pixabay, a community where creators freely share their work under specific conditions. Through guided practice, students search for images and respond to questions that demonstrate their understanding that verifying usage rights is not optional – it’s a responsibility.
Get Ready to Make the 3D Model
Now that students have shown they can use images responsibly and respect copyright, it’s time for the exciting next step of transforming a picture into a 3D model with the help of generative AI. The model will be an eye-catching addition to the science fiction story.
Finding the right tools for schools wasn’t simple. TechnoKids explored a range of options to uncover free, student-friendly 3D modeling apps. Want to know which ones made the cut and how to use them successfully in your classroom? Don’t miss my next post with our top recommendations and practical teaching tips for teaching AI and digital citizenship.